Broad beans, faba beans and fava beans are all denominations referring to a variety of beans highly appreciated in the Mediterranean as well as Asian cuisines and culture: Vicia faba. Fava beans are one of the oldest crops in the world and historical documents suggest the beans have been extensively cultivated since ancient times. They are extremely rich in vitamins, minerals and other phytochemicals and the high concentration of essential nutrients in the beans is a source of some amazing properties and health benefits for health.
Despite being genuinely nutritious, fava beans are also a source of side effects, one of which stands out. Fava beans can cause a potentially fatal condition called ‘favism’. Favism is often inherited and more common in certain parts of the population for whom consumption of the bean is strongly advised against, despite being a truly wonderful supply of vitamins and minerals. This article will tell you all you need to know about fava beans and how this legume affects your health.

What do fava beans look like?
Fava beans or broad beans are similar in appearance to most other bean varieties: a small to medium-sized elongated pod enclosing 4-10 broad, kidney-shaped to round beans of a light green color. When ripe, the fava bean pods will occasionally tinge brown or black in some places. If left to dry, the beans turn almost completely brown. Fava beans are relatively easy to grow and can easily thrive in one’s back garden with little to no care (except for watering and weeding). The plant can reach outstanding heights of up to 6 meters and gets its first flowers in as little as 1 month after having been sowed.
What do fava beans taste like?
Fava beans are famous for their somewhat nutty, not too sweet, pea-like flavor. Green fava beans are more tender, but the dry variety makes for some amazing tasting dishes as well. You can eat fava beans straight off the vine and they taste pea-like, overall pleasant with green flavor notes.
Fava beans nutrition facts and benefits
Fava beans are an excellent source of protein: 100 g of fresh broad beans provides a little over 26 g of protein, while 100 g of cooked fava beans have around 7.6 g of protein. A helping of slowly simmered fava beans with parsley, lemon juice, a pinch of salt and olive oil can be an excellent way of supplying the body with the proteins required as part of a healthy, balanced diet. Plus, it’s delicious!
Even more, fava beans are rich in fiber which promotes regular bowel movements, thus providing an easy, natural remedy against constipation. In addition to this, fiber rich foods such as walnuts, almonds, white beans, kidney beans, peas, fava beans and other legumes help reduce cholesterol levels by preventing the absorption of fat at the intestinal level, which also promotes weight loss.

Like all legumes, fava beans contain great amounts of fiber, in this case 25 g of fiber/100 g of raw beans and 5.4 g of fiber/100 g of boiled and drained fava beans.
When consumed in moderate amounts, fiber is good for the body and its slightly laxative effect helps maintain the health of both our intestines and colon. Additionally, eating fiber-rich foods such as fava beans is believed to reduce the risks of colon cancer by reducing the time our colon is exposed to waste material.
But remember: an extremely high intake of fiber can have bad effects on your health as well because it may limit the absorption of vitamins and minerals, interact with medicine absorption and irritate the stomach, causing or worsening an existing gastritis.
Fava beans bring important health benefits due to their unique plant sterols content. Numerous scientific studies confirm the fact that plant sterols, natural compounds found in plants, efficiently lower LDL (bad) cholesterol levels, promoting cardiovascular health. Cholesterol in the blood can be reduced on average by 7% to 10.5% if a person consumes 1.5 to 2.4 grams of plant sterols [and stanols], states the European Food Safety Authority in a publication from 31 July 2009. Even more, consuming fruits, vegetables, nuts, cereals and legumes such as fava beans continuously can help maintain LDL cholesterol levels low.
Fava beans also contain genistein and daidzein. These two isoflavones appear to regulate hormone metabolism and lower the incidence of breast, ovarian and prostate cancer. However, the Shanghai Breast Cancer Survival Study suggests that a moderately high intake of isoflavones appears to have significantly reduced breast cancer risks in Asian women and men alone. Some studies have advanced conflicting results, stating that genistein and daidzein may promote breast tumor growth when paired with tamoxifen, a medicine used in both breast cancer therapy treatment and prevention. Although eating legumes on a regular basis will not likely cause any major hormone imbalances, it is important to have all the information there is on the foods you like to eat on a regular basis.
Fava beans and favism
Fava beans can be fatal to a small part of the population suffering from glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency, a medical condition now known as favism. Basically, favism means that the body is predisposed to hemolytic anemia (destruction of red blood cells) as a reaction to certain foods, fava beans included, or malaria medication. The condition is usually accompanied by jaundice. Interesting enough, although favism is a potentially fatal condition, it appears to offer protection and, sometimes, complete immunity against malaria. If you have never eaten fava beans (or broad beans) ever before, my advice is to act with caution and talk to your doctor first.
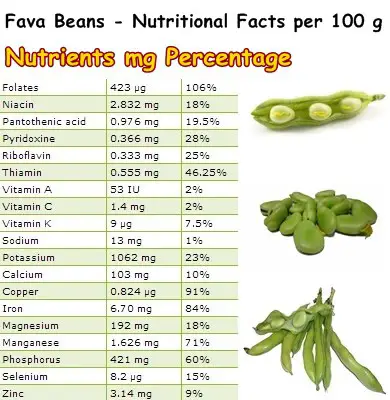
Fresh fava beans are an unbelievably rich source of folate (or vitamin B9). Folate is recommended during conception and pregnancy to prevent neural tube defects in newborns. In addition to this, folate is essential for cell DNA synthesis, cell repair and division. Approximately 100 g of raw fava beans provide 106% of the RDA of folate (or vitamin B9). Fava beans are also an excellent source of thiamine, riboflavin and pyridoxine, B vitamins which help coordinate muscle and nerve activity (thiamine), promote healthy skin (riboflavin) and support the production of amino acids.
As you can see in the table above, fava beans contain generous amounts of calcium, copper, iron, magnesium, potassium, manganese, phosphorus, selenium and zinc. Iron (84%) supports the production of red blood cells and prevents anemia. Copper (91%) prevents premature graying. Manganese (71%) has powerful antioxidant effects. Potassium regulates heart pressure and magnesium supports the activity of every muscle in the body, including the heart.
List of health benefits of Fava Beans
Here is what fava beans are good for health-wise:
- Building muscle thanks to a high protein content that supports muscle repair processes.
- Helping synthesize neurotransmitters for the brain and nervous system from the amino acids that make up protein, with direct benefits for mood, sleep and focus.
- Helping maintain a steady weight thanks to a high protein, low fat content.
- Eating fava beans combats fatigue and raises energy levels as a result of a rich B vitamin content.
- Fava beans support and boost learning and help combat brain fog thanks to B vitamins and a high protein content.
- Benefits for high blood pressure owed to a good potassium and magnesium content.
- Benefits for muscle cramps, eye twitching and leg cramps at night.
- Rich source of iron, good for anemia and associated side effects, including tiredness and fatigue, pallor, muscle weakness and more.
- Free radical-scavenging benefits via antioxidants such as copper, iron and manganese.
- Good food to eat for thyroid health thanks to its selenium content.
Conclusion
Overall, fava beans have a generous vitamin and mineral content, as well as provide numerous other phytochemicals with outstanding antioxidant properties and various health benefits. In certain parts of the world, they are a major part of many people’s diets, providing important amounts of protein for muscle growth, nervous system health and energy metabolism, fiber for digestive health and weight management, B vitamins for digestion, skin and brain health as well other essential vitamins and minerals with important antioxidant and anti-inflammatory functions.
