As their name suggests, pine nuts are the seeds of pine tree cones. There are several edible varieties which differ slightly in length, width and shape, but which all preserve a fragrant nutty aroma. Pine nuts are a great source of essential nutrients such as vitamin B1 and vitamin E, manganese, magnesium, phosphorus, iron, zinc and copper with cardiovascular, nervous system and digestive benefits.
Moreover, they boast a high content of healthy monounsaturated fatty acids that help lower blood cholesterol levels and improve cardiovascular health.
Monounsaturated fatty acids are a healthy kind of fat and are also found in olive oil and other vegetable oils.
Additionally, pine nuts have been shown to helps curb hunger and food cravings, offer antioxidant protection to cells and improve muscle function. Taking into account their nutritional profile, regular consumption can further contribute to improved energy levels, digestive benefits, strong bones and anemia management and prevention.

Edible pine nuts
Here is a list of edible pine nut seeds: the stone pine or Pinus pinea, Pinus cembra, Pinus sibirica, Pinus bungeana, Pinus sabineana, Pinus coulteri, Pinus lambertiana, Pinus pumila and Pinus armandii. The seeds collected from all of the above-mentioned varieties are edible and, unlike those of other species, they distinguish themselves in terms of length, width and shape. Shelled pine nuts are small, elongated, usually thin, creamy white seeds with a hard texture and distinct nutty flavor.
What do pine nuts look and taste like?
Depending on the variety, they may be more or less plump, but usually only the biggest seeds are commercialized for consumption purposes. Pine seeds are protected by a hard brown outer shell which is not edible. They are called pine nuts because they look like smaller versions of a nut and because of their nutty taste.

What are the benefits of Pine Nuts?
As far as their health benefits are concerned, pine nuts boast a high nutritional value, a characteristic of most nuts and seeds. Their nutty flavor is a result of their high fat content, containing around 68 g of fat/100 g. Although they may not seem very figure-friendly, pine nuts are actually extremely healthy because they contain mono and polyunsaturated fatty acids, two good types of fat. A type of monounsaturated fatty acid is oleic acid, renowned for decreasing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
Numerous studies suggest that the Mediterranean diet, characterized by a rich intake of monounsaturated fatty acids, greatly favors healthy blood lipid profiles, thus lowering the risks of heart disease and stroke. Eating pine nuts and other nut and seed varieties is therefore extremely beneficial for cardiovascular health. Pine nuts also contain Omega-6 fatty acids and pinolenic acid.
According to more recent research, pinolenic acid causes the activation of two enzymes that suppress hunger: cholecystokinin and glucagon. This basically decreases appetite and promotes weight loss. Despite their high caloric value (673 kcal/100 g), it appears that pine nuts help promote weight loss naturally. Nevertheless, they should be consumed with moderation because calories are still calories and they will add up to extra kilograms over time.
Pine nuts are a great source of vitamin E, containing 62% of the RDI. Vitamin E maintains healthy mucous membranes and protects both the lungs and the skin from damage caused by reactive oxygen molecules called free radicals. Moreover, pine nut oil, also a great source of vitamin E, can be used topically as a natural remedy for dry skin and related problems, provided you are not allergic to pine nuts.
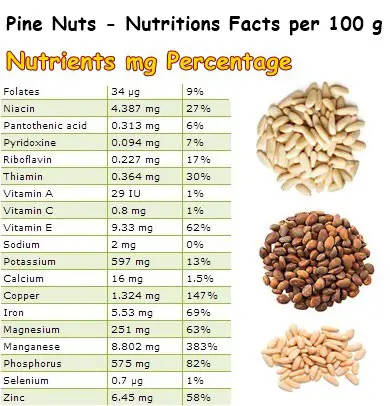
In addition to this, pine nuts contain good amounts of thiamine, niacin, riboflavin, folic acid, pyridoxine and pantothenic acid. B vitamins ensure the proper synthesis of fats, proteins and carbohydrates, a process resulting in energy for the body and elevated energy levels. Moreover, B vitamins are vital for brain and nervous system health, supporting cognitive performance. Lastly, they play an important role in skin health. For example, vitamin B3 (niacin) deficiency can lead to dermatitis, swelling and hair loss, all signs of a more serious condition known as pellagra.
Pine nuts provide excellent amounts of minerals as well. Manganese (383%) is a potent antioxidant. Copper (147%) prevents anemia and improves sleep quality. Magnesium (63%) increases calcium absorption in bones and supports muscle activity, heart included. Iron (69%) prevents anemia, irritability and fatigue. Zinc (58%) strengthens the immune systems. All of these health benefits and more can come from pine nut consumption.
What are the side effects of Pine Nuts?
There have been multiple reports in the past few years of people experiencing a strange metallic taste in the mouth after eating pine nuts. The taste is reported to last for up to a few days after consumption of the nuts.
This rare phenomenon is called pine mouth syndrome and has yet to be explained. A bad mouth taste can have other causes as well, including but not limited to acid reflux disease, stomach ulcers, medication side effects, heavy metal toxicity and more. However, it appears to be triggered by eating a particular variety of Chinese pine nuts (Pinus armandii) and may last up to a couple of weeks.
Nevertheless, if you notice unusual symptoms after eating the seeds, discontinue consumption and seek medical help immediately. If you suspect you may be allergic to them, it is wise to have a skin allergy test before eating the seeds to rule out a potential allergy. Also, make sure you know where your seeds come from so you can avoid an unpleasant experience such as pine mouth syndrome. Other than this, it would be a pity not to enjoy all the wonderful health benefits pine nuts have to offer.
