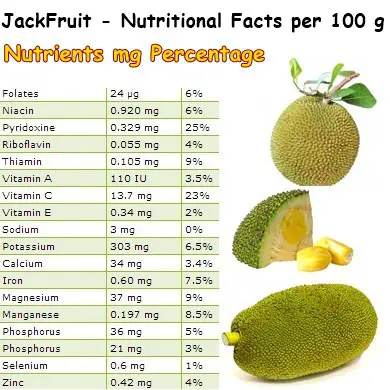
Did you know that watermelons grow on trees? Well, they do and their name is jackfruit. This Asian borne fruit is related to the mulberry family and is a favorite among tropical fruits. Jackfruit are a great source of vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C, vitamin B6, manganese, iron, magnesium and potassium, nutrients with a beneficial action on blood pressure, muscle health, digestion, energy levels and immune system health.
Regular consumption is said to benefit the cardiovascular and digestive systems, improve immunity, reduce inflammation and offer antioxidant protection to cells and DNA. Moreover, jackfruit is a good source of dietary fiber and thus contributes to relieving constipation, managing hemorrhoids and maintaining colon health. Having a high carbohydrate and sugar content, the fruit offers quick energy and can help prevent hypoglycemia.

What does jackfruit look like?
Jackfruit are enormous, bright green, prickly fruit, quite similar in appearance to durian or a giant mulberry. The inside is made up of numerous golden-yellow bulbs of pulp called pods which cloak a chestnut-sized red-brown seed each. Jackfruit may weigh between 3-34 kg and reach 1 meter in length. The number of seeds varies depending on the size of the fruit, but a medium-sized jack has somewhere between 50-500 seeds. Jackfruit pulp and seeds are both edible. Also, it should not be confused with durian, a close look-alike, but entirely different fruit.
What does jackfruit taste like?
Unripe, green jackfruit pulp has a meaty, chicken-like taste which is why it is sometimes referred to as meat for vegetarians. However, jackfruit has a low protein content and isn’t the best option for anyone looking to meet their protein requirements from plant sources. Legumes and nuts are far better sources than jackfruit in this respect.
Ripe jackfruit tastes sweet, with a pineapple and banana flavor and a slight mango fragrance. It has a soft or slightly chewy, fibrous, crisp texture, reminiscent of hard apples. Its sweet, fruity smell might lead one to believe it is overripe and thus not suitable for consumption, when it just smells sweet. Although ripe jackfruit might not smell very fresh, remember that it does not mean they are overripe. They just have a slightly funny smell to them.

See also: Is Jackfruit Acidic?
Jackfruit vs durian
Differences and similarities between jackfruit and durian
Jackfruit is actually very similar in appearance to durian, although a trained eye will spot the difference between the two immediately. First of all, both fruits are large and can grow to impressive sizes.
They both have a greenish yellow color and a sometimes not-so-pleasant smell. However, the jackfruit is covered in harmless small bumps, while durian has thorns that can hurt the skin.
Jackfruit has small, edible seeds, while durian has large, edible seeds, one for every segment of flesh.
Durian pulp is also perfectly organized inside the fruit in segments called seed pods, so that cutting it open allows for clean eating, but that of jackfruit is harder to get to because it is mixed with inedible portions of fiber and attached to a sticky middle part. While jackfruit fresh is yellow, durian’s can be yellow, orange and even pink or reddish. The texture of the flesh is crisp in jackfruit, and soft in durian. Lastly, jackfruit has a more fruity aroma, reminiscent at times of overripe, spoilt fruit, while durian has a pungent, unpleasant smell that deters most people from eating it.
Also see benefits of durian.
Remember that jackfruit are quite sticky so you may want to prepare yourself a pair of scissors or a knife and some disposable gloves to help you reach the pods and not have to struggle with the sticky white milk (latex) oozing from the fruit. Also, it would appear that a little vegetable oil can do wonders when peeling and cutting a jackfruit. Unripe jackfruit is great for curry, while the ripe pulp is best frozen, stir-fried, boiled or made into a delicious iced milkshake. The seeds can be boiled, roasted or baked. You know you’ve had the real jackfruit experience when you taste a pulp as sweet as honey.
You might be interested : Jackfruit vs Breadfruit
Benefits and uses of jackfruit
As far as its health effects are concerned, jackfruit boasts the following uses and benefits:
Provides instant energy
Jackfruit pulp contains simple sugars such as fructose which are assimilated fast and provide almost instant energy. Simple sugars are basically easily digestible carbohydrates that are turned into glucose (a type of sugar) soon as they are digested. Glucose is then used to give energy to our brain, muscles and heart and power basic life-sustaining processes.
A serving of 100 g of raw jackfruit pulp provides 23.25 g of carbohydrates, out of which 19.08 are natural sugars. While it is great for a non-diabetic to get quick energy, the fruit is not the best option for diabetics as it can raise blood glucose levels too much too fast. Find out more about jackfruit and its effects for diabetics in the article: Is jackfruit good for diabetes?
Great laxative properties
Jackfruit is one of those foods which help prevent constipation naturally. Not only does it have a good fiber content (1.5 g of fiber/100 g of pulp), but it is also about 73% water, and thus regulates intestinal transit time and prevents constipation. The fiber in the pulp makes stools bulkier, while the water, which is absorbed by the fiber, makes them softer. Eaten it excess, it can cause side effects such as painful abdominal cramps, bloating, loose stools and diarrhea.
This ensures easier bowel movements and leads to good intestinal motility which, in turn, maintains colon health and helps manage hemorrhoids. Because jackfruit is not at arm’s length to everyone, you can rely on a carrot and honey juice. Just 200 ml (6.8 oz) of this will send you running to the toilet in no more than 90 minutes.
Boosts immunity and reduces inflammation
With 23% of the RDA of vitamin C, jackfruit helps the body develop resistance against viral infections, accelerates wound healing and efficiently reduces inflammation markers, a preceding factor for chronic disease.
Offers antioxidant protection
Vitamin C, manganese as well as several polyphenols found in the golden pulp and seeds of the jack fruit provide great antioxidant protection from reactive oxygen molecules called free radicals. Together, they remove harmful free radicals from the body and prevent them from damaging healthy cells.
Maintains healthy, beautiful skin
Jackfruit provides 25% of the RDA of pyridoxine, or vitamin B6. Pyridoxine not only maintains healthy lymphoid organs (responsible for good immunity), but also prevents skin problems such as eczema. Also, the good vitamin C content of the fruit stimulates the production of collagen, a protein in our body which keeps our skin firm, young and wrinkle-free.
Promotes cardiovascular health
Jackfruit provides small amounts of magnesium (9%) and potassium (6.5%), two extremely heart-friendly minerals. Magnesium maintains the health of the heart muscle by ensuring it receives electrical impulses from the brain telling it to beat regularly while potassium efficiently regulates blood pressure and body fluids.
About jackfruit seeds
They are a good source of vitamins and minerals and just as easy on the stomach as the fruit. Harvest them from fully ripe fruit then bake, boil or roast them to your liking. Traditional medicine recommends jackfruit seeds for ulcers and other digestive problems. Overall, the fruit is a tropical delight and a much pleasant culinary experience than its twin, durian.
