Did you know there are white watermelons? Unless you know beforehand, you won’t know they are white inside until you crack them open to eat them.
You can eat white watermelon just like any other watermelon color and enjoy similar benefits for health. While lacking in lycopene, xanthophylls and other carotenoid antioxidants, nutrition wise, white watermelon is a source of citrulline with circulatory benefits, potassium and magnesium with anti-hypertensive benefits and contains good amounts of vitamin C with anti-inflammatory and antiaging benefits and benefits for teeth and gums health.
White watermelon is fruit part of our list : 25 white fruits and vegetables
Are there white watermelons?
Is there such a thing as a white watermelon? Believe it or not, white watermelons are real. They are the same fruit as the more common pink and red fleshed watermelon varieties, just white inside.
What does it mean when watermelon is white?
There are two main possibilities when it comes to white watermelon fruit: either the fruit is not ripe yet, hence the white flesh, or it’s simply a different variety of watermelon with white flesh instead of pink or red, or yellow or orange.
Yes, there are also yellow watermelons and orange watermelons, not just white, pink and red. There is also a similar looking white citron watermelon (Citrullus caffer, Citrullus amarus) that is related to the sweet white watermelon (Citrullus lanatus).

What does a white watermelon look like?
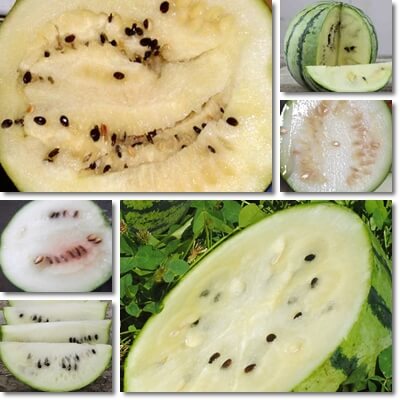
White watermelon fruit are just like regular watermelons, except that they are white inside. White watermelon have an oblong or rounded shape with light green rind with medium to dark green stripes varying in thickness running along the length of the fruit, and range in size from one kilogram to several. Despite the name white watermelon, white watermelons are not always completely white, or very white.
Some varieties of white watermelon have snow-white flesh, others are more of a cream-white color, but there are also white watermelons with white and some degree of light pink flesh. White watermelon seeds are chewy and cream colored when immature, and brown to black with a hard shell when mature.
Can you eat white watermelon?
Just because your watermelon is white inside, that doesn’t mean you can’t or shouldn’t eat it. White watermelon is perfectly edible and safe to eat, and you can eat it raw, cooked or pickled. In fact, you can eat white watermelon fruit whole: the white part of the watermelon rind, the hard green outer rind, the flesh and seeds.
What does white watermelon taste like?
The taste of white watermelon fruit is not always consistent. If the fruit is perfectly ripe and has enjoyed optimal growing conditions (i.e. sunlight, temperature, water), it should taste sweet, with a typical watermelon flavor profile. The flesh should be crisp, juicy and refreshing. White watermelon varieties such as White Sugar Lump watermelon, White Wonder watermelon, Cream of Saskatchewan watermelon and Japanese Cream-Fleshed Suika are reported to have the sweetest taste.
If the watermelons are not fully ripe or have not enjoyed optimal growing conditions, they may not taste sugary-sweet, but rather faintly sweet with cucumber flavor notes, maybe somewhat citrussy.
Are white watermelons genetically modified?
White watermelons are not genetically modified organisms (GMO). They actually occur naturally, as a result of selective plant breeding efforts. White watermelon fruit are thought to precede the modern pink and red fleshed varieties. In fact, a few thousand years ago all watermelons had a greenish-white, hard and rather unpalatable flesh, more like modern day white citron melons, aka white citron watermelons. As a result of cultivation efforts, watermelon slowly became sweeter, less dense and crisper, as well as developed new flesh colors (pink, red, yellow, orange).
Why are white watermelons white inside?
What does it mean when a watermelon is white inside? Simply put, white watermelons have little pigment to their flesh. What makes red watermelon red inside is a type of red carotenoid pigment called lycopene. Yellow watermelon is yellow inside because of yellow carotenoid pigments called xanthophylls (e.g. lutein, zeaxanthin, neoxanthin, violaxanthin, neochrome). Orange watermelons owe their flesh color primarily to orange carotenoid pigments such as beta-carotene.
By comparison, white watermelon is low in red, orange and yellow pigments that give other varieties their colors.
White watermelon nutrition facts and benefits
White watermelon flesh contains very little lycopene, lutein, zeaxanthin and other pigmented carotenoids which normally are sources of benefits for eye health, skin, immunity and blood pressure. Other than this, the nutrition of white watermelon is similar to that of other colors.
For instance, white watermelon is good source of vitamin C, providing around 10% of daily requirements for every 100 g of fruit (flesh only). Vitamin C has anti-inflammatory properties, promotes the health of gums and teeth, and boosts collagen production for better skin elasticity and younger-looking skin.
White watermelon is essentially sodium-free and a modest source of magnesium and potassium (under 5%) with minor benefits for high blood pressure. The white part of the watermelon rind contains citrulline with benefits for high blood pressure and vasoprotective properties (see the benefits of citrulline for blood pressure).
A modest source of vitamins B1, B2, B5, B6 and iron, white watermelon has anti-anemia benefits, helping support red blood cell production and muscle oxygenation for improved vitality and more energy. High in water, it combats dehydration and related side effects such as headaches, dizziness, tiredness and fatigue. White watermelon also has diuretic properties and supports normal kidney function, and is low in calories and fat making it good for healthy weight loss. Source of organic sugars and dietary minerals and electrolytes, white watermelon helps combat low blood sugar and has tonic properties.
