Red sweet potatoes are a variety of yams with red or red purple skin and red, yellow, pink or cream flesh. Red sweet potato types are a source of good nutrition and rival orange fleshed varieties when it comes to benefits for health. Eating red sweet potatoes is good for high cholesterol and high blood pressure, helps combat tiredness and anemia and contributes to lower risks of cataract.
What are red sweet potatoes?
Red sweet potatoes are sweet potato varieties with a red, red-brown, pink-red or red-purple skin color and flesh that is not orange, copper, purple or violet. While there are different varieties of red sweet potatoes, the most popular are Japanese red sweet potatoes, also called Asian or Oriental red sweet potatoes, and Northern Star red sweet potatoes.
However, nomenclature may differ considerably. Since sweet potatoes are named both after their skin color and flesh color, this can cause the same variety to be called by different names. For example, types of red sweet potatoes with yellow flesh are also commonly called yellow-fleshed sweet potatoes. Color perception can further result in different names. For example, Japanese red sweet potatoes which have a red to red-purple skin are also commonly called Japanese purple sweet potatoes.
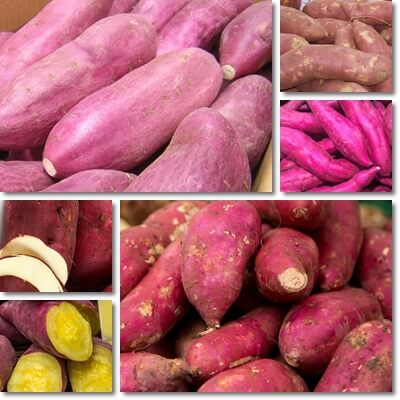
What do red sweet potatoes look like?
Red sweet potatoes are types of sweet potato with dark red, red-brown, pink-red or red-purple skin and pink, red, yellow, cream or white flesh. The general rule is that either the skin or the flesh has to be red or a shade of red. Types of red sweet potatoes with red, red-brown, pink-red or red-purple skin and yellow flesh are the most common and considered by some to be the typical red sweet potato, while varieties with pink and red flesh are rarer.
What do red sweet potatoes taste like?
The taste of red sweet potatoes can differs according to variety. Types of red sweet potatoes with pink and red flesh tend to be moist, soft and fluffy in texture after cooking, and have a pleasant sweet taste of moderate intensity. Types of red sweet potatoes with white, cream, beige or very pale yellow flesh are on the drier side, somewhat starchier, and taste less sweet. Whereas red sweet potatoes with bright yellow and golden yellow flesh are somewhere in between, with a somewhat firmer consistency after cooking, and mild sweet taste.
See also : Can You Eat Red Potato Skin?
Red sweet potatoes vs orange
What is the difference between orange sweet potatoes, or yams, and red sweet potatoes? Orange fleshed sweet potatoes, also commonly called yams, can have orange to orange-brown, copper or even reddish skin, but always have orange flesh. Red sweet potatoes can have red, red-brown, pink-red or red-purple skin color and flesh that ranges from pink and red to golden yellow, pale yellow and even beige and white.

Red sweet potatoes nutrition
There isn’t much information available on the nutritional value of red sweet potatoes specifically. However, with a few exceptions, red sweet potato types have a similar nutrition as the more common orange fleshed sweet potatoes. The biggest difference between red sweet potatoes vs regular orange sweet potatoes (yams) is the the latter are higher in orange carotenoid antioxidants with vitamin A activity such as beta-carotene.
This difference in antioxidants profile and content brings about differences in nutrition as well:
- Red sweet potatoes are generally lower in vitamin A than orange fleshed sweet potatoes which have the highest content of vitamin A of all types of sweet potatoes.
- Types of red sweet potatoes with golden flesh are high in yellow carotenoid xanthophyll antioxidants such as lutein and zeaxanthin, and contain smaller amounts of orange carotenes with vitamin A activity such as beta-carotene and alpha-carotene.
- Red sweet potatoes with pink and red flesh have a higher overall and more varied antioxidants profile: orange and red carotenes, yellow xanthophylls, red and purple proanthocyanidins and anthocyanins, and other flavonoids and phenolic acids (salicylic acid, protocatechuic acid, chlorogenic acid, vanillic acid, gallic acid, caffeic acid).
- The darker the flesh color, the higher the antioxidants content.
- Types of red sweet potatoes with pale yellow, cream or almost white flesh have little to no vitamin A activity and have an extremely low content of pigmented antioxidants such as carotenoids and anthocyanins, if any.
Other nutrition facts of red sweet potatoes:
- moderate energetic value of only 80 to 90 kilocalories per 100 g
- high carbohydrates content at 12 g of carbs per 100 g
- good content of dietary fiber: 3 g of fiber per 100 g
- moderate to low sugar content: 4-6 g of sugars per 100 g
- around 1-1.5 g of protein and less than 0.5 g of fat per 100 g
- good content of vitamins B5, B6 and manganese (between 10% and 15% of daily requirements, RDI)
- good content of vitamins B1, B2, B3, magnesium, potassium, iron and phosphorus (between 5% and 10% of RDI)
- low content of calcium, sodium and zinc, vitamin C, vitamin E and folate or vitamin B9 (under 4% of daily recommended intakes)
Red sweet potatoes benefits for health
- Provide quick energy: carbohydrates in red sweet potatoes raise blood sugar levels for an almost immediate boost in energy.
- Constipation relief: eating red sweet potatoes provides good amounts of dietary fiber to restore normal transit and favor easy and regular bowel movements that are easy to pass.
- Benefits for blood pressure: eating red sweet potatoes is good for high blood pressure thanks to a good potassium and magnesium content in the potatoes which help lower blood pressure numbers that are too high.
- Other cardiovascular benefits: eating red sweet potatoes can help improve cholesterol values, and the vegetable is a good option for anyone with high cholesterol.
- Good food to eat for losing weight: red sweet potatoes can be included in the diet in moderation to help with weight loss and reduce body fat.
- Combat tiredness and fatigue: red sweet potatoes have a good content of B vitamins and iron to boost energy metabolism and combat physical tiredness and mental fatigue and boost productivity.
- Good food for anemia: red sweet potatoes have a good content of vitamin B6 which helps produce hemoglobin and boosts the capacity of hemoglobin to absorb oxygen, actively helping combat anemia.
- Red sweet potatoes with pink and red flesh are high in anthocyanin antioxidants with scientifically proven anticancer properties.
- Red sweet potatoes with golden yellow flesh have a good content of lutein and zeaxanthin antioxidants which lower risks of cataract and AMD (age-related macular degeneration).
- Even though red sweet potatoes are high glycemic with a glycemic index of 70, diabetics can eat them in moderation. The sweet potatoes have dietary fiber, complex carbohydrates and can be paired with a source of protein and fat to limit their effects on blood sugar.
- Red sweet potato greens are edible and safe to eat, and provide benefits for vision, skin and immunity. They are good for high blood pressure and have a depurative action. See more benefits of sweet potato leaves.
Red sweet potatoes side effects
Red sweet potatoes are generally safe to eat and have little to no side effects. Side effects are typically minor and associated with excessive intakes on a background of pre-existing medical conditions. Eating red sweet potatoes too frequently or in too high amounts is contraindicated for people with high blood sugar, diabetes and obesity.
