Tuna is a healthy fish, full of benefits for health. The benefits of tuna stem from its excellent nutritional profile, with nutrition facts such as a high protein content and a high content of vitamins B3, B12 and D, phosphorus, selenium and iodine taking precedence. Eating tuna can help you lose weight and boost fertility and pregnancy rates, as well as exerts immunomodulating effects, reducing susceptibility to infection and autoimmune diseases, among other benefits.
1- Tuna is a nutritionally dense food
Tuna is naturally high in vitamins B3, B12 and D, phosphorus, selenium and iodine. The oily fish is also a high protein food, and high in healthy unsaturated fats such as Omega-3 fatty acids. Not just this, but tuna has a good content of choline, vitamin A, iron, magnesium, potassium and zinc. All of these nutritional facts considered, tuna ranks as one of the top nutritionally dense foods to eat.

2- Eating tuna is good for weight loss
Light tuna varieties and tuna canned in water and in brine are low in calories with less than 100 kcal (kilocalories) per 100 grams. The low energetic value recommends tuna as a good food to eat for weight loss. However, if you are looking to lose weight, avoid tuna canned in oil which has close to 250 calories for every 100 grams.
3- Tuna is a natural source of vitamin D
One of the biggest benefits of tuna is the fact that it is a source of vitamin D. Tuna is one of the few types of foods that naturally have vitamin D, and regular consumption can help replenish low vitamin D levels. Just 100 grams of tuna can get you between 33.5% and 45% of your daily vitamin D values.
Find out more about the vitamin D content of tuna.
4-Tuna is minimally processed
Tuna is generally a minimally processed food, available as raw, fresh fish, smoked, or canned in brine, in water or in oil. This is a positive thing as eating foods that are minimally processed is good for health, not to mention the fact that the lack of complex processing helps preserve the essential nutrients food intact.
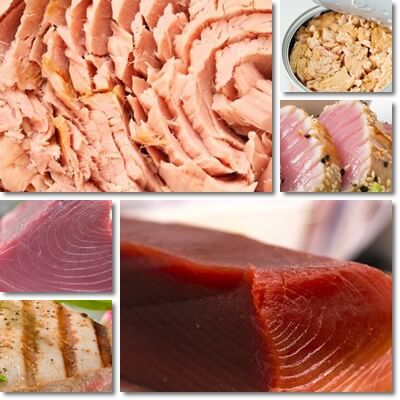
5-Eating tuna helps the body make vitamin D
One of the benefits of eating tuna is that it helps the body make its own vitamin D, in addition to providing it in generous amounts. Tuna is a source of cholesterol which the body uses to make vitamin D through exposure to ultraviolet radiation from sunlight.
Find out more about the benefits of sun exposure.
6-Eating tuna helps improve bone density
Tuna naturally has vitamin D and high amounts of it. One of the functions of vitamin D is to maintain calcium, magnesium and phosphate homeostasis, essentially regulating and optimizing the absorption of the minerals in bones and teeth. Eating tuna thus boosts bone mineralization for better bone density and stronger, healthier bones and teeth.
7-Tuna is a good food to eat for osteoporosis
Tuna is a good food to consider eating to reduce osteoporosis risks. For one, tuna is high in vitamin D which regulates the absorption of minerals into bones for better bone density.
Tuna also provides modest to generous amounts of several minerals that go into the composition of bones, including phosphorus, calcium and magnesium, actively contributing to building bones.
8- Eating tuna is good for building muscle mass
If you are looking to build more muscle, then tuna is a good food to consider. With 22 to 29 grams of protein per 100 grams, tuna is naturally high in protein, as well as contains complete protein with all essential amino acids. Eating tuna helps you gain muscle easily by providing the raw material for new muscle acquisition.
9- Eating tuna is good for memory and learning
Tuna provides, on average, 8 grams of fat per 100 grams, including saturated, polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fat. The fat from tuna, especially polyunsaturated fatty acids such as DHA Omega-3, is used by the brain to both build brain matter and support brain activity, notably cognitive functions such as memory and learning. Eating foods that are naturally sources of fat, especially fish and seafood which have DHA Omega-3 fatty acids, not just supports cognitive functions, but can also help delay cognitive decline.
10-Tuna protects the nervous system
Tuna from clean sources, that is, tuna that is uncontaminated by mercury and other heavy metals, actually has a protective effect on the nervous system. The fish species provides high amounts of vitamin B12 and cholesterol which are used to produce myelin. The myelin sheath is a protective coating insulating the tail of nerve cells called neurons, preventing leaks in electrical impulses and improving brain-body communication. Deterioration of the myelin sheath has been linked to degenerative diseases of the nervous system such as multiple sclerosis.
11- Good food to eat for anemia
If you have anemia, then of the best foods you can eat is tuna. Tuna has a high content of vitamin B12 and good amounts of iron which are needed to make new red blood cells and help red blood cells transport oxygen, improving vitality and boosting energy levels. Just 100 grams of tuna can get you between 79% and 393% of all the vitamin B12 you need in a day, and between 5.5% and 7.7% of your daily iron values. Find out more about tuna nutrition.
12- Tuna feeds the brain and supports a good mood
The fat and protein in tuna nourish the brain, helping you think clearer and better, and boost mood. Fats from tuna, particularly healthy polyunsaturated fats such as DHA Omega-3 fatty acids, combat brain fog and promote clear thinking, improving memory and focus. The amino acids that make up the protein in tuna are used as raw materials to synthesize neurotransmitters which regulate mood, helping elevate a low mood and improve disposition.
13- Eating tuna boosts the immune system
Tuna is a high protein food with 22 to 29 grams of protein per 100 grams. The immune system makes use of proteins which it uses for the immune system response. Antibodies, inflammatory and anti-inflammatory proteins that are part of the immune system response are sourced from high protein foods such as tuna.
Moreover, tuna is naturally high in vitamin D which studies show has important immunomodulating effects. According to research, vitamin D targets several different types of immune cells, ‘including monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, T-lymphocytes and B-lymphocytes, modulating both innate and adaptive immune responses’ (source).
Getting enough vitamin D from sun exposure and from foods such as tuna and other fish high in vitamin D can reduce susceptibility to infection and autoimmune conditions by modulating the immune system response.
14- Tuna has cholesterol lowering properties
Tuna is naturally high in vitamin B3: just 100 grams of tuna covers between 50% and close to 100% of daily vitamin B3 values for an adult, depending on tuna species. High amounts of vitamin B3, more exactly, the vitamin B3 form known as niacin, also found in tuna, has been shown to exert cholesterol lowering effects. Niacin has been shown to lower both triglyceride and LDL (bad low density lipoprotein) cholesterol levels in the blood.
15- Tuna is good for thyroid health
Fish and seafood such as tuna are good dietary sources of both iodine and selenium. Both iodine and selenium are vital for thyroid health, modulating thyroid activity and the production of thyroid hormones. Getting enough of both in your diet is the key to good thyroid and general health.
16- Eating tuna boosts fertility and conception rates
Tuna is not normally recommended to women who are pregnant or looking to conceive because of concerns of heavy metal contamination, notably mercury contamination.
However, tuna can actually boost fertility and increase conception rates, not to mention it can be consumed safely during pregnancy, without any adverse reactions, so long as intake is reasonable.
For one, tuna is high in vitamin D – studies show low vitamin D levels are associated with poor fertility, especially in women, and even infertility. Getting enough vitamin D, whether it’s from sun exposure, dietary sources or supplements, can help boost fertility and increase conception chances.
Tuna is also high in iodine and selenium. For one, iodine and selenium support the activity of the thyroid gland which has a strong regulatory effect on the entire endocrine system – low levels of thyroid hormones are associated with infertility, especially in women, and a common cause behind low conception rates.
Also, iodine helps with the normal development of the baby during pregnancy – low levels of iodine are known to cause intellectual disability. Lastly, selenium can help clear contaminants such as mercury, rendering foods such as oily fish (e.g. tuna, salmon) safe to eat during pregnancy, in limited amounts of course.
Talk to your doctor about how much tuna you can eat during pregnancy, and make sure you choose tuna low in mercury (choose varieties such as skipjack over yellowfin, and research fishing locations to make sure your tuna comes from a safe fishing zone, low in contaminants).
17- Tuna is an anti-inflammatory food
Tuna can be considered an anti-inflammatory food. For one, it’s high in vitamin D which has known immunomodulating effects, with a focus on anti-inflammatory activities. Tuna is also high in unsaturated fatty acids, notably polyunsaturated fatty acids such as DHA Omega-3 which has scientifically proven anti-inflammatory benefits. Lastly, tuna is high in selenium which helps clear mercury and other contaminants, helping cancel out the side effects associated with heavy metal contamination.
