Blueberries are one of the best types of berries to eat.
Naturally, they are preferred fresh, but when they’re out of season or simply just not available, know that the next best thing to fresh is frozen.
Frozen blueberries are, for the most part, just as nutritious as fresh ones, with only negligible differences that do not impact daily nutritional values measurably.
And because serving sizes in grams, while exact, are not everyone’s cup of tea, today we’re going to be analyzing the nutrition of one cup of frozen blueberries which is about 150 grams of the frozen, unthawed berries.
Of course, you can also check out the nutrition facts for 100 grams of frozen blueberries as well as the nutrition facts for 100 grams of fresh blueberries.

Nutrition facts for 1 (one) cup of frozen blueberries:
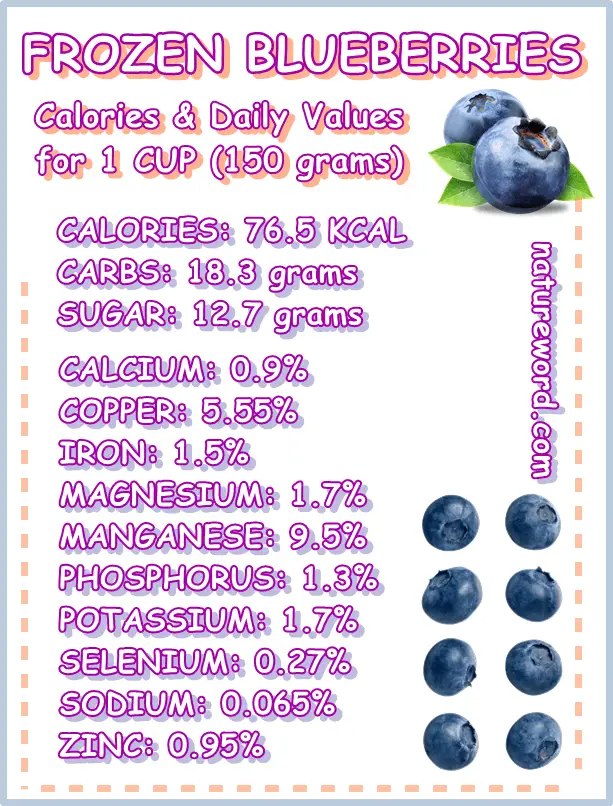
- Energetic value (calories): 76.5 kcal (kilocalories)
- Carbohydrates content: 18.3
- Sugar content: 12.7 grams
- Fiber content: 4.05 grams
- Protein: 0.63 grams
- Fat content: 0.96 grams
- Water content: 130 grams
Vitamins in 1 (one) cup of frozen blueberries:
- Vitamin A: 3 micrograms (mcg) from pigmented beta-carotene antioxidants, but no retinol
- Vitamin B1: 0.048 milligrams (mg)
- Vitamin B2: 0.055 milligrams
- Vitamin B3: 0.78 milligrams
- Vitamin B5: 0.1875 milligrams
- Vitamin B6: 0.088 milligrams
- Vitamin B9 (folate): 10.5 micrograms (mcg)
- Vitamin B12: 0
- Choline: 7.65 milligrams (mg)
- Vitamin C: 3.75 milligrams
- Vitamin D: 0
- Vitamin E: 0.72 milligrams (mg)
- Vitamin K: 24.6 micrograms (mcg) in the form phylloquinone
Minerals in 1 (one) cup of frozen blueberries:
- Calcium: 12 milligrams (mg)
- Copper: 50 micrograms (mg)
- Iron: 0.27 milligrams (mg)
- Magnesium: 7.5 milligrams
- Manganese: 0.22 milligrams
- Phosphorus: 16.5 milligrams
- Potassium: 81 milligrams
- Selenium: 0.15 micrograms (mcg)
- Sodium: 1.5 milligram (mg)
- Zinc: 0.105 milligrams
Nutrition facts from USDA.gov.

Frozen Blueberries: Daily Values for 1 (One) Cup
- Energetic value: just 3.8% of the daily calorie intake for the average adult
- Carbohydrates: under 6.65% of daily requirements for an adult person
- Dietary fiber: 14.5% of daily requirements
- Protein: just 1.26% of daily requirements
- Fat: 1.23% of daily requirements
Vitamins in Frozen Blueberries: Daily Values for 1 (One) Cup
- Vitamin A: 0.33% of daily values of vitamin A for the average adult person
- Vitamin B1: 4%
- Vitamin B2: 4.2%
- Vitamin B3: 4.9%
- Vitamin B5: 3.75%
- Vitamin B6: 5.2%
- Vitamin B9: 2.625%
- Vitamin B12: 0%
- Choline: 1.4%
- Vitamin C: 4.2%
- Vitamin D: 0%
- Vitamin E: 4.8%
- Vitamin K: 20.5%
Minerals in Frozen Blueberries: Daily Values for 1 (One) Cup
- Calcium: 0.92% of daily calcium values for the average adult person
- Copper: 5.55%
- Iron: 1.5%
- Magnesium: 1.785%
- Manganese: 9.5%
- Phosphorus: 1.3%
- Potassium: 1.72%
- Selenium: 0.27%
- Sodium: 0.065%
- Zinc: 0.95%
Note: The nutrition facts presented above are determined for a cup of frozen, unthawed, unsweetened blueberries which is roughly about 150 grams.
Note: Blueberries are not very nutritious judging by how little they contribute to the daily nutritional requirements of the average adult.
The bulk of their health benefits comes from their high antioxidant content which is a source of important anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anticancer and antidiabetic effects.
