What is the potassium content of cooked potatoes? Do baked potatoes have more potassium than French fries? Do fried potatoes have less potassium than boiled potatoes?
Do potatoes with skin have more potassium than potato flesh? Do potato skins have any potassium at all? Which is the best kind of cooked potatoes to eat to get as much as possible of your daily potassium?
How much potassium in cooked potatoes?
- There are, on average, 451 to 478 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of oven-heated, pre-cooked French fried potatoes.
- There are 535 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of baked potatoes, flesh and skin.
- There are 792 milligrams of potassium in one standard serving of baked potatoes, flesh and skin (148 grams per serving).
- There are 391 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of baked potatoes, flesh only (no skin).
- There are 573 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of baked potato skins (potato skin only).

- There are 545 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of baked red potatoes, flesh and skin.
- There are 550 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of baked russet potatoes, flesh and skin.
- There are 544 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of baked white potatoes, flesh and skin.
- There are 372 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of roasted potatoes (general values).
- There are 379 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of boiled potatoes, flesh only (potatoes cooked in skin).
- There are 328 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of boiled potatoes, flesh only (potatoes cooked without skin).
- There are 407 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of boiled potato skin.
- One potato skin (estimated weight: 34 grams) provides 138 milligrams of potassium.
- There are 447 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of microwaved potatoes, flesh and skin (cooked in skin).
- There are 296 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of home-made mashed potatoes with whole milk.
- There are 284 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of home-made mashed potatoes with whole milk and butter.
- There are 1200 to 1535 milligrams of potassium in 100 grams of unsalted chips.
Note: The potassium content is the same for salted and unsalted versions. However, using salt with take away from the benefits of potassium as potassium and sodium from salt have opposing properties. Too much sodium from salt limits the benefits of potassium.
Note: Potassium values for the different types of cooked potatoes are from USDA.gov
Also see what is the potassium content of raw potatoes per unit and 100 grams.
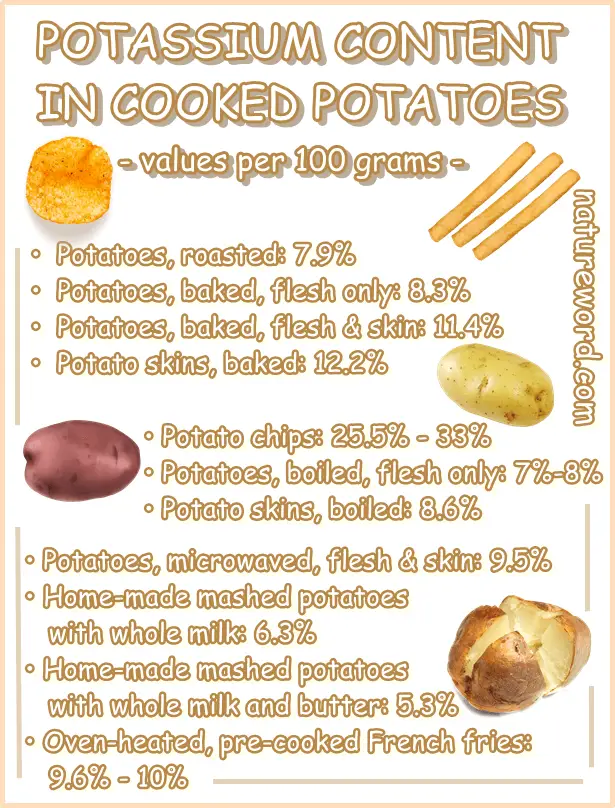
How much do cooked potatoes contribute to daily potassium?
How much of your daily potassium values can you get from different types of cooked potatoes? See below how much potassium there is in 100 grams of fried, baked, boiled, roasted and mashed potatoes!
Oven-heated, pre-cooked French fries: 9.6% to 10%
100 grams of oven-heated, pre-cooked French fried potatoes provides 9.6% to a little over 10% of daily values for the average adult person.
Baked potatoes, flesh and skin: 11.4%
100 grams of baked potatoes with flesh and skin provides close to 11.4% of daily potassium values for the average adult person.
One serving of baked potatoes at 148 grams (flesh and skin) provides 16.85% of daily potassium values for the average adult person.
Baked potatoes, flesh only: 8.3%
100 grams of baked potatoes, flesh only, provides 8.3% of daily potassium values for the average adult.
Baked potato skins: 12.2%
100 grams of baked potato skins provides around 12.2% of daily potassium values for the average adult.
Baked red potatoes, flesh and skin: 11.6%
100 grams of baked red potatoes, flesh and skin, provides 11.6% (approximated from 11.595%) of daily potassium values for the average adult person.
Baked russet potatoes, flesh and skin: 11.7%
100 grams of baked russet potatoes, flesh and skin, provides 11.7% of daily potassium values for an adult person.
Baked white potatoes, flesh and skin: 11.6%
100 grams of baked white potatoes, flesh and skin, provides 11.6% (approximated from 11.57%) of daily potassium values for an adult person.
Roasted potatoes: 7.9%
100 grams of roasted potatoes provides 7.9% of daily potassium values for the average adult.
Boiled potatoes, flesh only: 7% to 8%
100 grams of boiled potatoes, flesh only, but boiled with skin, can get the average adult 8% of all the potassium they need in a day.
100 grams of potatoes, flesh only, boiled without skin, can get the average adult 7% of all the potassium they need in a day.
A good tip is to eat boiled potatoes with boiled eggs for balanced nutrition – while the potatoes account for the carbohydrate part of the meal, and provide generous amounts of potassium in particular, the boiled eggs provide the fat and protein for a perfectly balanced meal.
Discover the surprising benefits of eating boiled eggs and find out what is the nutrition of just one boiled duck egg.
Boiled potato skins: 8.6%
100 grams of boiled potato skins can get the average adult 8.6% of all the potassium they need in a day.
1 boiled potato skin weighing an estimated 34 grams can get the average adult 2.9% of all the potassium they need in a day.
Microwaved potatoes, flesh and skin: 9.5%
100 grams of microwaved potatoes, flesh and skin, can get the average adult about 9.5% of all the potassium they need in a day.
Home-made mashed potatoes with whole milk: 6.3%
100 grams of home-made mashed potatoes with whole milk can get the average adult around 6.3% of all the potassium they need in a day. But because the standard serving size is at least double than that, the actual potassium intake from eating mashed potatoes is higher.
Using low-fat 1% or 1.5% or non-fat 0.1% dairy milk such as cow’s milk can up the potassium content of the dish. Fat that is removed from milk is replaced with the liquid portion of the milk. Potassium is water soluble and found in the liquid portion of milk which means that the lower the fat content of dairy milk, the higher the potassium content.
Also see how much potassium in milk from sheep, goat, water buffalo and camel and discover what are the benefits of drinking camel milk for health.
Home-made mashed potatoes with whole milk and butter: 5.3%
100 grams of home-made mashed potatoes made with whole milk and butter can get the average adult 5.3% of all the potassium they need in a day. However, you actually get more potassium from the dish because the standard serving size for mashed potatoes is at least double.
Tip 1: Use low-fat or, better, non-fat 0.1% milk to boost the potassium content of the dish.
Tip 2: You can add cooked spinach or beet leaves to your mashed potatoes for a boost in potassium content.
How much potassium in spinach? A serving of 100 grams of raw spinach provides close to 12% of daily potassium values for an adult, while the same amount of cooked spinach provides close to 14% of daily potassium for an adult. Find out more about the potassium content of spinach.
Beet leaves have even more potassium – just 100 grams can get you around 16% of all the potassium you need in a day.
Potato chips: 25.5% to 33%
A serving of 100 grams of potato chips provides, on average, between 25.5% and 33% of daily potassium values for an adult person. Ideally, go for unsalted chips because the high amounts of salt usually added to chips are enough to cancel out all the benefits of potassium.
Conclusion
Boiled, baked, roasted and grilled potatoes are all great options to get your potassium from. You can even eat potatoes every day (they make a great substitute for bread, pasta and rice).
Even mashed potatoes can be consumed daily, if intake is reasonable and the dish is made from scratch using ingredients in their utmost natural state (e.g. dairy milk, butter).
Do avoid adding too much salt and limit frequency of intake for processed options such as pre-cooked French fries, and various other shapes and cuts of pre-cooked potato fries.
If possible, avoid frying and cook them in the oven on a baking sheet.
If chips is something you insist on having, it’s best to go for unsalted options.
Instead of adding salt on your chips or fried, you can opt for a sprinkle of sweet or hot paprika or even smoked paprika, garlic powder, onion powder, ground pepper, or have them with pickles for prebiotic benefits. Pickled cucumber and pickled beets are delicious options.
