Cucumbers (Cucumis sativus) have managed to preserve a somewhat privileged place on our table and today I am going to speak to you about why it’s good for your health to keep eating cucumbers.
Relatively recent research suggests that cucumbers are a moderately nutritious and overall healthy vegetable.
The biggest benefits reside in the high water content which counteracts dehydration and promotes diuresis with benefits of blood pressure.
The culinary vegetable contains small amounts of several B vitamins, potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, phosphorus and zinc which give it tonic, energizing properties.
Cucumbers are a good source of vitamin K for atherosclerosis prevention and contain no sodium, adding to their cardiovascular benefits. With small amounts of vitamins A and C, they hold benefits for skin and boost immunity.

Cucumbers are mentioned in various ancient writings, which can be seen as proof that ancient civilizations such as the Mesopotamian people, the Romans, the Indians and the Greek were insightful to the curative properties this ordinary vegetable possesses.
While they do not boast an amazing nutritional value, they do contain certain compounds with several surprising health benefits.
The cucumber (also known as Cucumis sativus) is a close relative of the cantaloupe, watermelon, zucchini and pumpkin. It is widely cultivated throughout the world which is why we can easily find it in many modern cuisines.
Though pickled cucumbers are much more popular than the fresh vegetable, pickling involves massive use of salt and vinegar, taking away from its health effects.
Those of you who like this vegetable in particular and have some free time and a little garden space gain the most if you plant a few vines. This way you can have your own organic cucumbers of excellent quality.
As a garden plant, the cucumber does not require almost any attention at all once the seeds are sown.
What do cucumbers look like?
The cucumber is an elongated, cylinder-shaped vegetable, rounded at the ends and slightly curved. Because it can be picked at almost any growing stage, it can range in size from a few centimeters to gourd sizes of over half a meter in length.
While there are different cultivars with different characteristics, usually the most tender and tasty cucumbers are those picked before reaching maturity.
The more mature the cucumber, the larger its seeds and the tougher and more bitter its skin.
Most varieties have a dark green skin which can be smooth, bumpy or prickly. The inside pulp is crisp and has multiple medium sized to large translucent-white seeds.
What do cucumbers taste like?
Cucumbers taste watery, but have a pleasant crisp texture and faint green flavors. Overall, they are relatively bland. However, the more it is left to mature, the more bitter the cucumber may taste. The skin is slightly more flavored, with more pronounced green flavors, but can become bitter in older vegetables.

Nutrition facts and benefits Of Cucumbers
Cucumbers have been the object of extensive scientific research because they contain a potent natural compound called pinoresinol which has been found to be a highly effective anticancer agent and a source of important benefits for cardiovascular health, reducing risks of cardiovascular disease.
Not just this, but cucumbers are a modest source of essential vitamins and phytochemicals with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
The culinary vegetable also contains beta-carotene and several important minerals such as manganese and potassium and magnesium which are a source of minor cardiovascular benefits.
Studies show that cucumbers contain a substance called cucurbitacin, also found in most members of the Cucurbitaceae family.
Cucurbitacin is said to be a potent anti-inflammatory and analgesic that can also suppress carcinogenesis in skin cancers.
Unfortunately, some studies suggest curcubitacin may also possess cytotoxic effects, meaning it is toxic to cells in general. However, cytotoxic effects have been shown to appear only when extreme amounts of cucumbers are consumed.
In fact, the presence of cucumbers in our daily diet can actively and efficiently help prevent chronic disease by means of the powerful natural agents they contain, from antioxidants to essential vitamins, minerals and dietary fiber.
Quercitin, another highly potent antioxidant found in cucumbers, is a flavonoid and, according to researchers, boasts significant anti-inflammatory free radical-scavenging properties. I
n addition to reducing inflammation associated with high-risk illnesses and protecting against free radical damage, quercitin is used to improve physical endurance, lower cholesterol levels, manage cardiovascular disease, diabetes and treat respiratory infections.
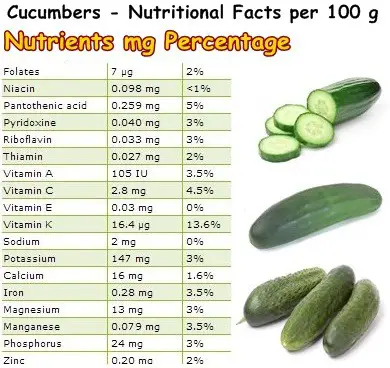
From a nutritional point of view, cucumbers contain good amounts of vitamins K, C and B5. Vitamin K is essential for proper blood coagulation and bone mineralization, while vitamin C is an excellent natural anti-inflammatory and antibacterial.
For further information, you can consult the nutritional table above. And because they are 90% water, have no sodium and are low in calories, eating cucumbers helps with weight management and prevents water retention.
This is also probably why they are recommended as a treatment for cellulite.
What is eating cucumber good for?
Below is a list of some of the best benefits for health of cucumber:
- Weight loss and better weight management as a result of a low energetic value (only 15 kcal/100 g).
- Rehydrating action, great food to eat when it’s hot outside.
- Constipation relief and a good food for hemorrhoids.
- Has no sodium, safe to eat for anyone with high blood pressure.
- Source of vitamin K to prevent nosebleeds and easy bruising.
- Helps lower cholesterol and provides benefits for diabetes sufferers.
- Tonic action and energizing effect as a result of a varied vitamin and mineral content.
- Source of antioxidant polyphenols with anticancer action.
- Anti-inflammatory properties and cardiovascular benefits.
