Parmesan cheese, also known as Parmigiano-Reggiano, is a staple cheese variety famous all around the world. It is a matured cheese with mild flavors and a delicate, refined taste profile, perfect for grating over pasta or rice dishes to which it imparts an exquisite savor. True parmesan cheese is a source of important nutrients, notably amino acids and protein, phosphorus and calcium, vitamin D, B vitamins and especially vitamin A. Despite its high content of sodium, eating parmesan in moderate amounts can be good for you.
What is parmesan cheese? Parmesan cheese is an Italian hard cheese variety made exclusively in Italy. The cheese is produced in several provinces in the Emilia-Romagna region in the Northeast of Italy and the province of Mantua in Lombardy, also in the North. True parmesan cheese can only come from these provinces and hols a PDO, protective designation of origin status as a result. The alternative name of parmesan cheese, which is Parmigiano-Reggiano, indicates the production areas and is often used as a synonym to parmesan cheese and stamped on actual cheese. However, only European legislation currently requires for a difference to be made between true parmesan cheese (or Parmigiano Reggiano) and generic parmesan cheeses or cheeses similar to parmesan.

So remember that the original parmesan cheese, Parmigiano-Reggiano, only comes from the Emilia-Romagna region in Italy and holds distinct properties and benefits that are unlike those of generic parmesan cheeses. Being an original product, it has a high standard of quality and is strictly regulated, hence its pricey cost and unique flavor profile. Other similar cheese varieties produced elsewhere are not real parmesan, despite legislation that may allow for the use of the name more freely, without meeting the same manufacturing standards or quality as the original.
For example, a cheese matured for 9 months or made with milk from cows fed anything but their natural diet which is grass, or containing less fat is not real parmesan, but a similar cheese. There is even a soy parmesan, but parmesan is not vegetarian and calling a soy-based imitation of cheese vegetarian parmesan or just parmesan is plain inaccurate. The same strict production rules also apply to other protected Italian cheeses such as buffalo milk mozzarella (see article Properties and Benefits of Mozzarella).
Generic parmesan vs Parmigiano-Reggiano
What is the difference between generic parmesan and Parmigiano-Reggiano? The difference between the similar cheeses and the original parmesan is in the details. The flavor and properties of the original parmesan, Parmigiano-Reggiano are a result of a costly, lengthy and well-regulated production process that ensures a quality, artisanal cheese product. Any similar product that differs from the original production process in any way is an imitation of parmesan, even though it might actually be a good cheese. If it’s not made from cow milk alone, if it’s made only from skimmed cow milk, if it has additives, if it’s not aged for at least 18 months or does not meet the traditional standards of production, then it’s not real parmesan.

Frequently asked questions
How is parmesan cheese (Parmigiano-Reggiano) made? True parmesan is made from unpasteurized cow milk, whey and rennet. The cows providing the milk are fed exclusively on grass and hay. Both whole and skimmed cow milk are used and the resulting cheese is submerged in brine, then aged for 18 to 30 months or more. The cheese is inspected regularly to check if it meets the characteristics of true parmesan. Ultimately, the rind is branded with the certification mark and the dotted name Parmigiano. Overall, it is a natural product with a complex production process.
What does parmesan look like? Parmesan is usually produced as wheels. One wheel of cheese may weigh anywhere from 33 to 40 kilograms. Each cheese wheel has a tough, natural rind of a pale, golden color. On the inside, the cheese is compact, hard and straw-colored, crumbly and soluble. Parmesan has a dense, gritty texture and simply melts with the food when grated.
What does parmesan taste like? Depending on the aging time, it may have a more or less grainy texture and a complex taste profile. Generally speaking, the cheese variety is said to have an umami taste, the newly discovered fifth taste meaning savory or delicious. Its content of glutamic acid gives it this particular flavor. However, the longer parmesan is aged, the more complex and more pronounced its flavors. A good parmesan has a visible nutty, meaty, sharp taste and grassy, piquant, leathery, cooked milk flavors with slight fruity notes.
Health benefits
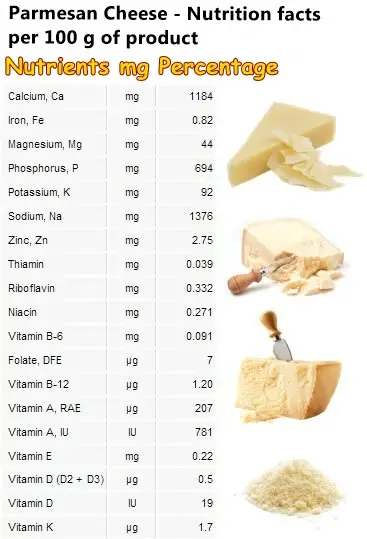
Is parmesan good for you? Parmesan is one of those foods that can be both good and bad for you, depending on how you use it and how much of it you eat. In moderate amounts, it is good for you because it adds protein, dietary minerals, vitamin A and small amounts of B vitamins and vitamin D to your diet. It is good for digestive health in particular. Too much becomes bad for you primarily because of its salt content.
Since the health effects of parmesan depend on how much of it you eat, here are the most notable properties and health benefits of eating parmesan in moderate amounts:
1) Easy to digest. Unlike meat which is digested in roughly 4 hours, parmesan cheese, also a source of complete protein, is digested in less than an hour. This is because its long aging time breaks down protein through fermentation and makes it easier to absorb, as if it were already partially digested. The gritty crystals you notice in parmesan are, in fact, proteins that have broken down into peptides (short chains of amino acids), peptones (containing more smaller peptides and other elements) and free amino acids, which are relatively easy to digest. However, it will cause stomach acidity and heartburn when eaten in excess or at night, close to bedtime.
2) Source of protein. Parmesan contains an estimated of 35 g of protein per 100 g, making it an excellent source of animal protein. We need protein in our diet for healthy hair, nails and other types of connective tissue, strong muscles and even cell-level functions such as cell signaling, DNA repair, immune responses etc.
3) Source of fat and cholesterol. Fat and cholesterol are not bad elements. We actually need both in our diet to survive and our brain in particular needs fats and some cholesterol to function optimally. It’s how much of them we get in our diet that matters. And eating parmesan moderately can actually be good for us.
4) Promotes digestive health. Parmesan is a fermented cheese and fermented products are known to help digestive health by feeding the good bacteria in our intestines. The cheese variety exerts prebiotic properties and, in moderate amounts, can be good for us.
5) Source of calories and energy. Yes, parmesan is a cheese and it provides more calories than vegetables or fruit. But it’s calories that give us energy and eating a bit of parmesan can boost our energy levels considerably. The shorter fatty acids chains it contains (a result of the lengthy aging process) are absorbed easily by the body and thus provide energy faster.
6) Source of vitamins and dietary minerals. Being a milk product, parmesan is a great source of vitamin A, required for good eyesight, healthy skin and good immunity. It also provides small amounts of vitamin D, needed for a strong immune system response and strong bones and B vitamins, required for energy metabolism. Parmesan is an important source of dietary minerals, especially calcium, phosphorus, but also potassium and magnesium and contributes to cardiovascular and bone health in particular.
7) Rich in sodium. By definition, parmesan is a matured cheese. But it’s also natural and what better way to preserve this cheese naturally for years than using salt? After all, we need sodium, salt to stay alive. Only when it’s consumed in excessive amounts it is bad for us. Eating a bit of parmesan now and then will not impact our health negatively because small amounts do not provide too much sodium. Also, parmesan does not contain gluten either.
Conclusion
Eating parmesan adds variety to one’s diet and provides good amounts of important nutrients such as vitamin A, B vitamins, calcium, phosphorus, potassium and magnesium. It benefits digestive, muscle, bone and brain health and boosts energy levels. What adds to its benefits is the fact it is entirely a natural product. Overall, parmesan is good for you as long as you eat it in moderate amounts occasionally.
