Tomato colors other than red are becoming increasingly popular, especially variegated varieties and dark-colored varieties such as blue tomatoes.
Believe or not, blue tomatoes are not exactly blue, and not entirely blue either. Blue tomatoes are essentially darker colored tomatoes with some degree of red-purple and even green or yellow skin and, often times, red-purple inside. Despite their unusual color, blue tomatoes are edible and perfectly safe to eat raw and cooked, not to mention a source of antioxidants and essential micro-nutrients with important benefits for health.
What is a blue tomato?
A blue tomato is a variety of tomato that ripens to a dark bluish color. Depending on the variety, blue tomatoes may be dark blue, black blue, purple blue or a dark indigo (somewhere between blue and violet). Some blue tomatoes have dark blue colored skin and flesh, while others have a dark bluish skin, but red or red-purple flesh.
Blue Tomatoes vs Purple Tomatoes ( What are The Differences?)
What is the difference between blue tomatoes and purple tomatoes? Some sources consider that blue tomatoes are the same thing as purple tomatoes, that is, tomato varieties of a dark blue-purple or blue-black color.
Other sources consider blue tomatoes to be a different type of tomato than purple, which would explain the distinctions in color between the two tomato colors clearly marked in the name of the variety (e.g. OSU Blue Tomato).
Indeed, most tomatoes of the purple type are more of a reddish color, purplish red to reddish brown. In general usage however, the names ‘blue tomato’ and ‘purple tomato’ are used interchangeably to refer to any and all tomato varieties of a dark color that is not red or black.
What do blue tomatoes look like?
There are actually several different varieties of blue tomato. There are both regular-size and cherry tomato varieties of blue tomatoes (e.g. OSU Blue Tomato, Bosque Blue tomato, Cherry Blue, Indigo Rose etc.). Some varieties are a uniform color on the outside, dark blue, purple blue or black blue all over, but there are also varieties that are an uneven color, dark blue or purple-blue with green, yellow or, more commonly, orange-red and red-purple.
Lastly, blue tomatoes can have dark bluish skin and flesh or a dark bluish skin with red or red-purple flesh. The pattern of color development may differ for fruits of the same variety according to growing conditions, with some blue tomatoes never reaching their true and final color for one reason or another.
What makes blue tomatoes blue?
What causes blue tomatoes to be a dark bluish color is a class of pigments known as anthocyanins. Anthocyanins are essentially pigmented antioxidants responsible for most red, blue, purple and black colors in our food. Upon exposure to sunlight, the anthocyanins in blue tomatoes darken which causes the tomato to turn a dark blue, purple blue or black blue color.
Aside from blue tomatoes, purple tomatoes and black tomatoes, eggplants, red raspberries, purple raspberries and black raspberries, blackberries, blueberries, chokeberries, purple carrots, black carrots, blue carrots, red and purple cabbage, black rice etc. are also sources of anthocyanins.
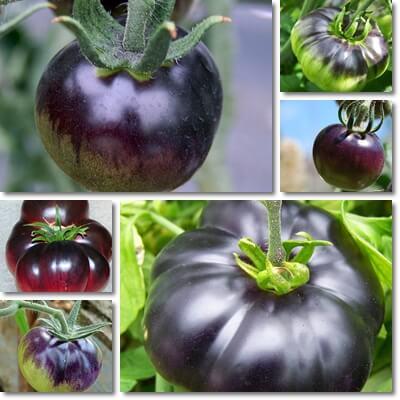

Why are some blue tomatoes red inside?
Actually, most varieties of blue tomato are not blue inside, but rather red or red-purple.
For example, the Indigo Rose, the Bosque Blue and quite a few other varieties of blue tomato have a dark-blue skin all over, or dark blue skin with some degree of red-purple, and red-purple flesh.
This is normal and both the dark blue peel and red-purple flesh are owed to anthocyanin pigments such as petunidin, malvidin and delphinidin. But the anthocyanin pigments from the peel are exposed to sunlight which causes them to darken, whereas the anthocyanins in the flesh are not exposed to sunlight which causes them to stay more red.
Can you eat blue tomatoes?
Yes, you can definitely eat blue tomatoes. All the different varieties of blue tomato are perfectly edible both raw and cooked and an important source of dietary micro-nutrients and antioxidants with wonderful benefits for health.
Blue tomatoes are an anticancer food, have blood pressure and cholesterol-lowering properties, anti-diabetic and anti-inflammatory effects. As for nutrition, they are a good source of vitamin C and B vitamins, potassium, manganese, phosphorus and magnesium and virtually sodium-free.
What do blue tomatoes taste like?
Blue tomatoes that are perfectly ripe and have received sufficient water, heat and direct sunlight should taste absolutely delicious: rich and earthy, with a sweet, flavorful, slightly acidic taste.
Blue tomatoes are slightly more astringent than red tomatoes as a result of their high content of anthocyanin antioxidants.
Lack of direct sunlight exposure on certain parts of the fruit can result in an inconsistent peel color, with dark blue, purple blue or black blue and red purple.
Are blue tomatoes GMO?
Some varieties of blue tomato are conventionally bred which means they were obtained by crossing tomatoes that naturally expressed some degree of anthocyanin synthesis. But because anthocyanin genes are not typically expressed in tomatoes as we know them, it took genetic engineering such as gene splicing to up anthocyanin expression in tomatoes and have them ripen to a dark blue, purple blue or black blue color.
Plenty of heirloom blue tomatoes are produced via conventional breeding and tend to be lighter colored and less ‘blue’, with the pigment typically restricted to the peel. Versus them, genetically modified blue tomatoes tend to have a more uniform, darker ‘blue’ color that is present in the flesh to some degree, as well as in the peel.
